Recent years have seen the Internet of Things (IoT) change how we live, work, and communicate. From smart homes to wearables, linked devices have made our lives easier and more efficient. As connected devices increase, so does data. Edge computing has emerged since the old centralized computing architecture has been strained. The global market of edge computing is set to generate $111 billion by 2028.
As technology evolves, edge computing becomes a powerful tool for promoting the IoT. Many companies are embracing edge computing to improve operations. This blog will address edge computing’s benefits for organizations and its impact on IoT to help corporate executives decide how to employ it.
Understanding Edge Computing in IoT
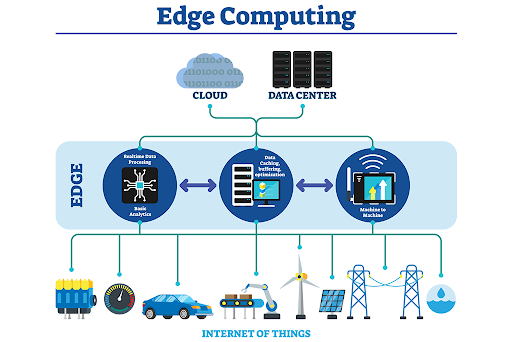
Edge computing processes data near its source, usually at the network edge, rather than using data centers or cloud infrastructure. Edge computing reduces data transmission to distant data centers for processing in IoT by bringing computation and data storage closer to devices and sensors. According to reports, Edge computing will see a significant increase in revenue rising to $210 billion by 2032. The number itself speaks for its relevance in the tech-driven world.
Edge computing in IoT is driven by the necessity for real-time processing and decision-making. Data traveling between IoT devices and centralized servers in traditional cloud computing models causes delay, which is unacceptable in applications like autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and healthcare monitoring systems that require split-second judgments.
Edge computing reduces latency and bandwidth utilization by placing computer resources closer to IoT devices, improving reaction times and network efficiency. It can also improve data privacy and security by processing sensitive data locally instead of sending it over the Internet to remote servers.
Some Essential Facts and Stats Related To The Edge Computing
- The edge computing addressable market will rise to US$445 billion by 2030.
- The Edge Computing Market is predicted to be worth USD 15.59 billion in 2024 and USD 32.19 billion by 2029, increasing at a CAGR of 15.60% over the forecast period.
- The edge computing market in the Middle East and Africa (MEA) region is expected to develop at a CAGR of more than 37% between 2024 and 2030.
- North America, Europe, and East Asia are expected to account for 88% of edge computing revenue by 2030.
- The market for edge computing applications is diverse, with many industries leveraging its capabilities to boost innovation and efficiency. The Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) has the biggest market share, at 30%.
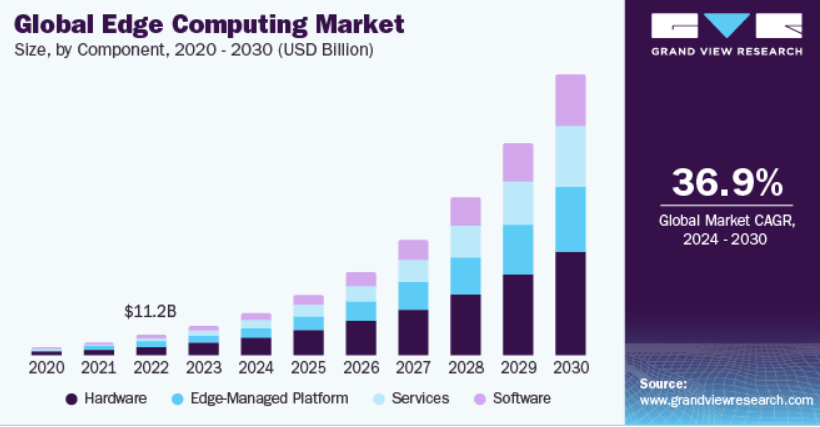
All these stats and figures indicate the edge computing market has a great future in the market. In the future, we may expect to see even more edge devices deployed, as well as edge computing employed for a broader range of applications. Edge computing is expected to play a significant part in the future of IoT, making it a fascinating technology to follow.
Benefits of Edge Computing in IoT Development
Edge computing in IoT development gives firms a competitive edge and opens new doors in numerous industries. Edge computing’s main IoT development benefits are listed below:
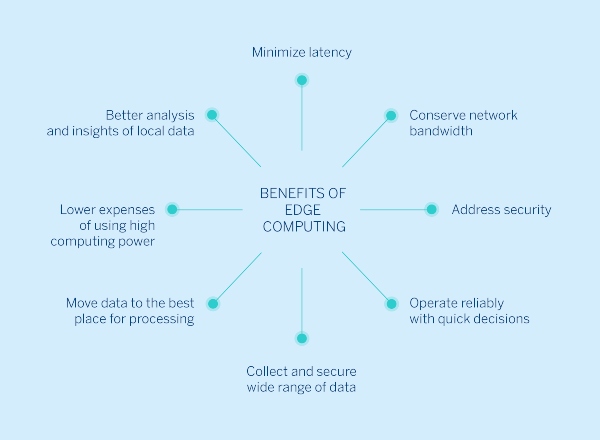
Reduced Latency:
Edge computing reduces latency by processing data closer to its source, which is a major benefit. Data must be sent between IoT devices and centralized servers in traditional cloud computing infrastructures, delaying processing and decision-making. Edge computing speeds up data flow by putting computation and storage closer to the network edge, enabling real-time or near-real-time response and analysis. Autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and healthcare monitoring systems require split-second choices; hence, latency reduction is essential.
Enhanced Privacy and Security:
Edge computing is designed to process confidential data near the resource rather than sending it to distant cloud servers over the Internet. This approach improves privacy and data security. The servers of traditional cloud computing design create a risk of breaching, interception, and unwanted access if sensitive data are sent on public networks. Edge computing lessens security threats by preventing secret data from being moved to the main network, or the disadvantage-indicated devices. The edge data safety and protection control is crucial to ensure the organization’s rule compliance and privacy are intact, as well as the security of sensitive data from unwanted access and attack by malicious threats.
Offline Operation:
Where intermittent network connectivity is concerned, edge computing complies with the principle of charging for the additional equipment and services and parties responsible for the operation of the IoT devices. Cloud processing can also not be suitable for meeting the needs arising from offline or industrial settings where intermittent connection is experienced. Edge computing solves this problem by enabling edge devices to suspend vital operations to situational servers without the need for constant connectivity to the centralized server. At the edge, devices can retain those key operations, collect valuable information, and execute prearranged actions offline, either being online or disconnected, processing data locally. Thus, the operation will not be disrupted, and the network will remain resilient.
Increased Reliability:
Edge computing decreases reliance on the cloud, making IoT systems more dependable and less likely to fail. Edge computing eliminates the requirement for internet connectivity by processing data locally, allowing IoT systems to operate even when the network is down. The rise of edge computing is a significant milestone in the evolution of the Internet of Things. It provides a more efficient, stable, and secure computing environment for IoT applications, opening up new avenues for innovation and expansion.
Applications of Edge Computing in IoT
Edge computing could be of help in industrial IoT appliances across multiple industries and use cases. Organizations can implement speed analytical and data processing and make prompt decisions, using less natural resources and generating more consumer-centric experiences through edge computing using real-time data across the network edge. Some significant IoT edge computing applications are listed below:
-
Smart Cities
The buzz that edge computing creates by making smart cities detect and solve traffic jams, ease congestion, and promote road safety due to its ability, to make it possible to perform traffic analytics in real-time. Intelligent traffic lighting systems with edge devices adjust traffic signal timings automatically to accommodate traffic patterns and congestion conditions, leading to less waiting time and traffic efficiency.
By placing them close to the physical infrastructure of the city, edge computing enables highly distributed environment systems of environmental sensors to observe air quality, noise, and other environmental parameters directly and react immediately. Cities, in turn, can discover pollution hotspots, mitigate environmental risks, and provide proper response by centralizing data from edge sensors.
Edge computing technology enables smart surveillance networks with real-time video analytic alerts that can detect and respond to security breaches, riots, and emergencies in real time. The edge devices may monitor real-time video feeds and insert information such as suspicious activity, license plates, and unusual activities into the system.
-
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Edge computing determines machine data from industrial equipment and devices or tests whether it is faulty or abnormal in an early stage, therefore avoiding a waste of funding. To decrease downtime and raise productivity, machines and facilities belonging to production plants and industries can be equipped with edge devices, which can be used to track equipment, estimate maintenance, and set maintenance.
Edge computing in industrial processes IIoT allows companies to review, improve, and respond to them remotely. Sensors and actuators embedded in edge devices can get raw data from industrial assets or local intelligence, thus acting as a deputy of the centralized station in decision-making. This way, industrial process improvement, especially complex ones, is optimized.
-
Healthcare
Edge computing focuses on collecting and analytics such as medical data, which could be received by wearable devices, medical sensors, health tracking devices, or IoT-enabled devices to enable remote patient monitoring. EDGE devices can locally process physiological data such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels and then relay the information to healthcare professionals for appropriate care at the right time. In this setting, the medical edge could lead to individualized treatment options, early recognition of conditions, and better patient results.
The edge computing capability lets medical devices enable accurate clinical analysis and also gives quick feedback to medical practitioners. These edge devices can interpret medical imaging, analyze biomarkers, or perform fast diagnostic tests on-site, which results in point-of-care diagnostics and even treatment with no need for centralized labs and fast patient care.
-
Retail
Edge computing evaluates and provides personalized recommendations about current targets while avoiding delays in decision time. Retailers can leverage edge devices for capturing with the aid of computers and analysis of customer purchase history, and demographics located at the store to have real-time data for target marketing and product placement optimization and to provide a better shopping experience to customers.
The Edge uses sensors to monitor stock levels, track product movements, forecast real-time demand, and many other things. Stations with RFID tags, barcode scanners, or sensors transmit local data and analyze it in real-time to make automatic replenishment orders and adjustments of inventories, thus optimizing stock levels, avoiding out-of-stocks, and preserving holding costs.
-
Autonomous vehicles
Edge computing reduces the time required to process, analyze, and map the information collected from cameras, LIDARs, radars, and other sensors. Hence, self-driving cars can make instant decisions based on such data. Sensors at the edge devices in self-driving cars can process information from the sensors, recognize objects, assess the various traffic situations, and steer, brake, or accelerate in a fraction of a second based on local computations without the need to keep connecting to the servers all the time.
In addition, autonomous car navigation systems utilize real-time road conditions, traffic congestion, and specific directions in roadways via edge computing. Edge equipment might assess live traffic data, determine arrival time, or prospectively warn drivers about track-ahead conditions. Computations concerning traffic congestion, closures, or accidents can also be made.
Read more: Benefits of IoT for business
Future Outlook and Trends
Edge computing will advance and develop fast thanks to revolutionary scientific achievements, vast infrastructure changes, and emerging IoT network ecosystem trends. Here are some IoT edge computing trends and predictions:
-
Edge AI and Machine Learning
The edge devices will be able to analyze data better, see patterns, and make decisions without human intervention due to the increased rollout of AI and ML algorithms in their functionality. Without centralized servers, perpetual connectivity, and air-tight security for regular updates, edge AI solutions let machines complete challenging tasks such as data stream analysis for anomaly detection and get actionable inputs in real time.
At the edge, more devices will process inference directly from sensors and locally extract data nuggets without forwarding massive raw data to far servers for analysis. ML models are trained locally on edge devices or previously trained in the cloud, which will lower latency, bandwidth, and IoT applications’ privacy and security.
-
Edge Security and Privacy
Edge computing deployments will be secured with privacy levels for any sensitive data stored or transmitted to reduce cyber threats. Organizations will apply secure bootstrapping, zero-trust architecture, hardware-based security features, and end-to-end security to achieve an all-inclusive security and compliance model in edge computing settings.
Differential privacy and homomorphic encryption will become more widespread in edge computing applications, contrary to their traditional purpose of protecting sensitive data and users’ privacy. The same will be true for secure multiparty computation. These techniques, which do not disclose sensitive or personal details, can provide information about the organization and its employees.
-
Edge-Driven Innovation
Advancement of edge computing will elevate new edge applications and services to a higher level with real-time insights and edge intelligence across industries. Now, edge innovation will change the use of technology, where products and services are performed in innovative experiences through the help of reality and predictive maintenance to tailor customers’ value.
Edge computing would make vertical-oriented apparatuses of smart manufacturing, precision agriculture, and connected healthcare feasible. In service, agri-industry, energy, automation, and numerous other industries, AI-enhanced IoT (Internet of things) solutions will increase analog enterprises’ productivity, efficacy, and sustainability, empower digitalization transformation, and provide a competitive advantage to such enterprises.
Read more: Iot Mobile App Development For Businesses
Drive innovation and growth to your business with Edge Computing.
Edge computing in IoT development, which brings data processing and connection to a new age, is a leading technology in the IoT field. This change is from centralized cloud infrastructures by eliminating long-distance data transport in favor of local, near-source processing, making IoT devices faster, more private, and more effective.
Are you struggling to make the most of technology? Parangat Technologies is here to assist with developing top-notch applications that contribute well to your brand and business growth. We have a team of dedicated developers well-versed in edge computing and IoT technologies to deliver the best solutions for your business that automate growth and streamline operations.
Contact us today to bring the idea of Edge computing to life.




